Table 1. In vitro Activity of Clindamycin Against Gram-Positive Aerobic Bacteria
|
Organism |
MIC90 Range (mg/L) |
MIC90 (mg/L) |
|
Bacillus cereus |
1 |
1 |
|
Listeria monocytogenes |
1 to 8 |
2.22 |
|
Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin susceptible) |
0.12 to 2 |
0.50 |
|
Staphylococcus saprophyticus |
0.12 to 0.25 |
0.16 |
|
Streptococcus agalactiae |
<0.06 to 0.50 |
0.15 |
|
Streptococcus bovis |
0.04 |
0.04 |
|
Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin susceptible) |
0.03 to 0.25 |
0.23 |
|
Streptococcus pyogenes |
0.13 to 0.25 |
0.19 |
|
Streptococcus spp. group B |
< 0.12 to 0.25 |
0.15 |
|
Streptococcus spp. group C |
< 0.12 to 0.50 |
0.22 |
|
Streptococcus spp. group G |
0.06 to 0.50 |
0.31 |
|
Streptococcus species, viridans Group (penicillin susceptible)
|
<0.06 to 1.6 |
0.53 |
Adapted with permission from Zambrano D, ed. Clindamycin in the treatment
of human infections. Kalamazoo, MI: The Upjohn Company, 1992.
Table 2. In Vitro Activity of Clindamycin Against Gram-Positive Anaerobic Bacteria
|
Organism |
MIC90 Range (mg/L) |
MIC90 (mg/L) |
|
Actinomyces species |
0.12 to 1 |
0.8 |
|
Clostridium botulinum |
4 |
4 |
|
Clostridium difficile |
4 to > 256 |
57.7 |
|
Clostridium perfringens |
0.25 to 8 |
3.4 |
|
Eubacterium species |
0.4 to 2 |
1.1 |
|
Lactobacillus species |
0.50 to 1 |
0.8 |
|
Peptostreptococcus |
0.12 to 4 |
3 |
|
Anaerobic Gram-positive cocci |
0.5 to 1 |
0.9 |
|
Propionibacterium acnes |
0.10 to 0.25 |
0.2 |
|
Propionibacterium species
|
0.12 to 0.20 |
0.16 |
Adapted with permission from Zambrano D, ed. Clindamycin in the treatment
of human infections. Kalamazoo, MI: The Upjohn Company, 1992.
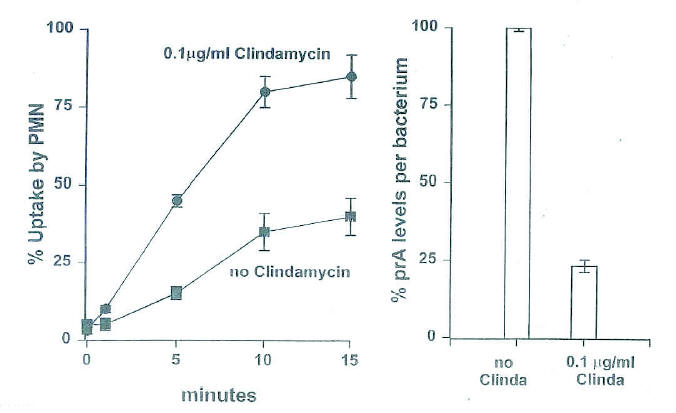
Figure 1. The chemical structure of lincomycin and clindamycin. (From Zambrano D, ed. Clindamycin in the
treatment of human infections. Kalamazoo, MI: The Upjohn Company, 1992. With permission).

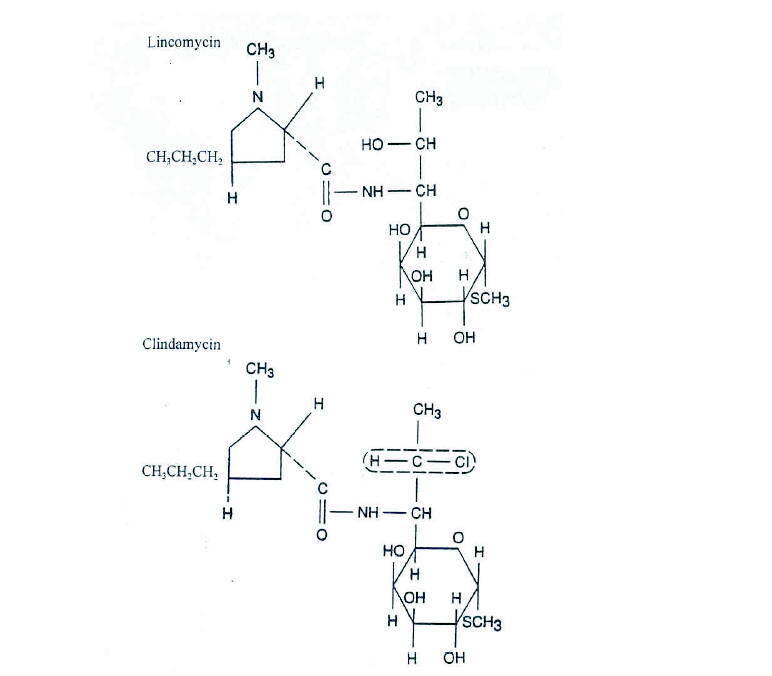
Figure 2. Average plasma concentrations of clindamycin obtained for six normal adult male volunteers following i.v. administration of 900 mg q. 8 h and 600 mg q. 6 h clindamycin phosphate sterile solution in a crossover study design. (From Zambrano D, ed. Clindamycin in the treatment of human infections. Kalamazoo, MI: The Upjohn Company, 1992. With permission).
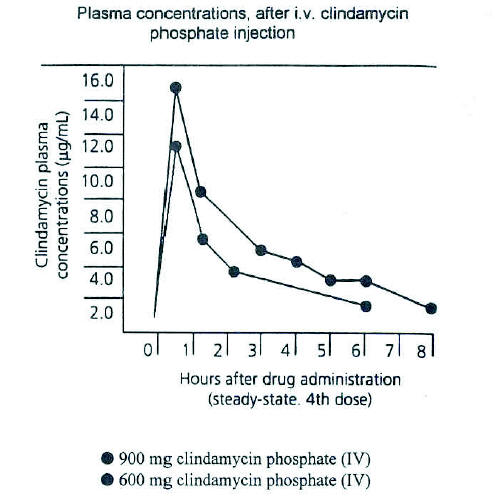
Figure 3. A. Average plasma concentrations of clindamycin obtained for 13 normal adult male volunteers following i.m. administration of 300 mg clindamycin phosphate sterile solution. B. Average plasma concentrations of clindamycin obtained for 22 normal adult male volunteers following oral administration of 300 mg clindamycin hydrochloride immediate after a meal. (From Zambrano D, ed. Clindamycin in the treatment of human infections. Kalamazoo, MI: The Upjohn Company, 1992. With permission).
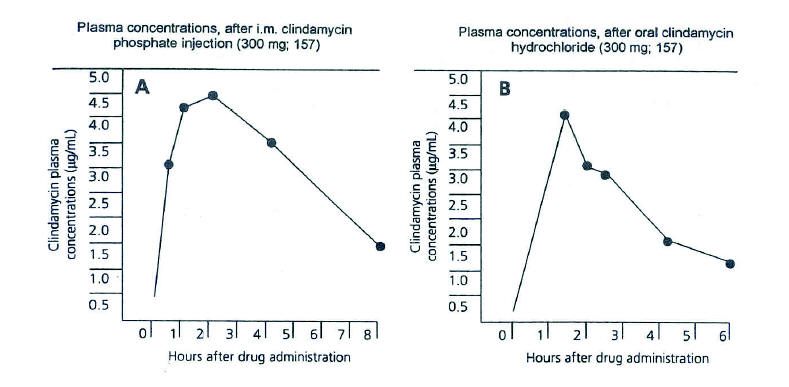
Figure 4. Subinhibitory concentrations of clindamycin enhances uptake of S. aureus by PMN and decreased protein levels in the cell wall. PrA, protein A.