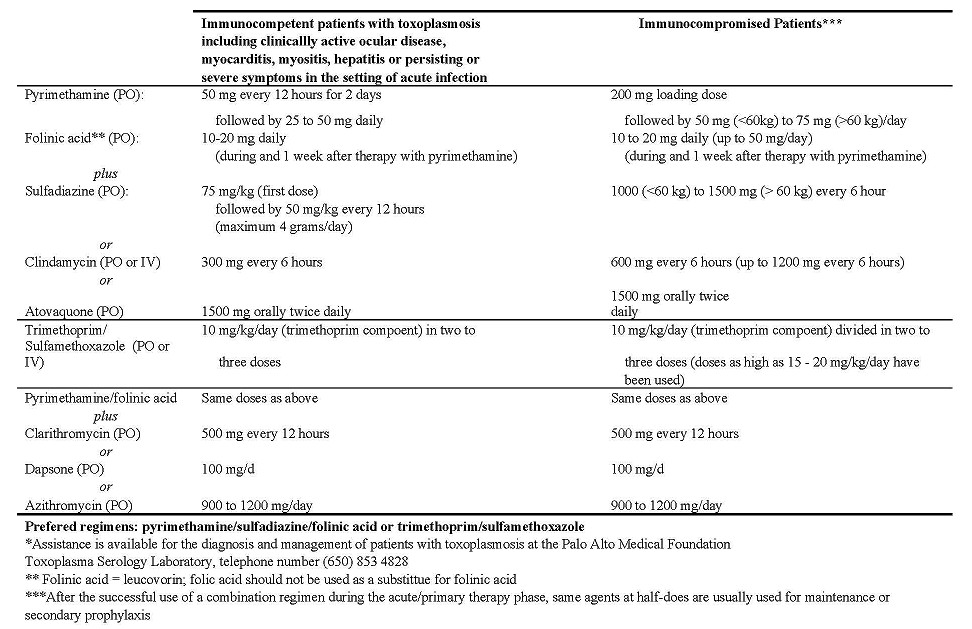
Table 1: Drugs Used in Immunocompetent and Immunocompromised Patients with Toxoplasmosis in the Setting of Acute Infection or
Reactivation* (Primary Therapy)

Table 2: Drugs Used in Pregnant Women Who Have Likely Acquired T. gondii Infection During Gestation and Infants Suspected or Confirmed
to have Congenital Toxoplasmosis
|
|
During Pregnancy |
In Congenital Disease |
|
Spiramycin (PO) |
Dose: 1 gram (3 million units) every 8 hours (for a total of 3 grams or 9 million units per day) Recommended for pregnant women suspected or confirmed of having acquired the infection < 18 weeks of gestation. Spiramycin should be administered until delivery in those with negative amniotic fluid PCR tests and negative follow up ultrasounds or low suspicion of fetal infection. Spiramycin is not teratogenic and it is available in the United States only through the Investigational New Drug (IND) process at the Food and Drug Administration [FDA, Administration [FDA, (301) 796-1600]. Prior consultation with medical consultants is required.* |
Not recommended during pregnancy if the fetus has been documented to be or suspected to have been infected (see below recommendations for pyrimethamine/sulfadiazine/folinic acid) |
|
Pyrimethamine (PO) plus sulfadiazine (PO) plus folinic acid (PO)
|
Dosages: Pyrimethamine: 50 mg every 12 hours for 2 days followed by 50 mg daily Sulfadiazine: 75 mg/kg (first dose) followed by 50 mg/kg every 12 hours (maximum 4 grams/day) Folinic acid** (leucovorin): 10-20 mg daily (during and for 1 wk. after pyrimethamine therapy) Recommended for women suspected of having acquired the infection at ≥ 18 weeks of gestation and those with positive amniotic fluid PCR test or abnormal ultrasound suggestive of congenital toxoplasmosis and patient is ≥ 18 weeks of gestation. Pyrimethamine is teratogenic and should not be used in pregnancy before week 18 (in some centers in Europe it is used as early as week 14). Sulfadiazine should not be used alone. |
Infant: (treatment regimen is usually recommended for one year) Pyrimethamine: 1 mg/kg every 12 hours for 2 days; followed by 1 mg/kg per day for 2 or 6 months; followed by 1 mg/kg per day every Monday, Wednesday, Friday Sulfadiazine: 50 mg/kg every 12 hr Prednisone (if CSF protein ≥ 1 gm/dL or severe chorioretinitis): 0.5 mg/kg every 12 hours (until CFS protein < 1 gm/dL or resolution of severe chorioretinitis)
Older children with active disease (usually 1-2 weeks beyond resolution of clinical manifestations) Pyrimethamine: 1 mg/kg every 12 hr (maximum 50 mg) for 2 days followed by 1 mg/kg per day (maximum 25 mg) Sulfadiazine: 75 mg/kg (first dose) followed by 50 mg/kg every 12 hours Folinic acid** (leucovorin): 10-20 mg three times weekly Prednisone (severe chorioretinitis): 1 mg/kg/d, divided bid, maximum 40 mg/d, rapid taper |
*Palo Alto Medical Foundation Toxoplasma Serology Laboratory, telephone number (650) 853 4828
or U.S. (Chicago) National Collaborative Treatment Trial Study (NCCTS), telephone number (773) 834-4152
** Folic acid should not be used as a substittue for folinic acid.