| |
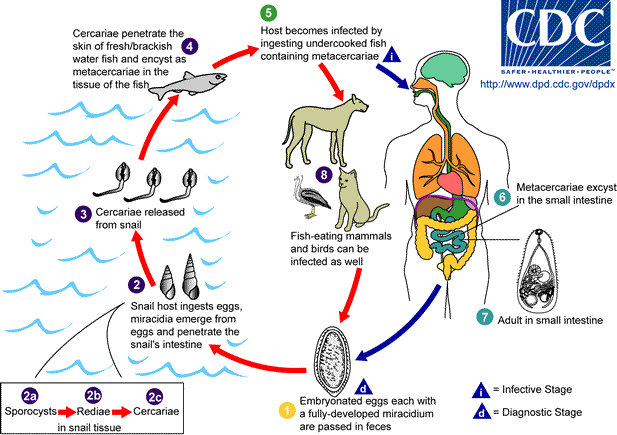
Adults release
embryonated eggs each with a fully-developed miracidium, and eggs are passed
in the host's feces
 .
After ingestion by a suitable snail (first intermediate host), the eggs
hatch and release miracidia which penetrate the snailís intestine .
After ingestion by a suitable snail (first intermediate host), the eggs
hatch and release miracidia which penetrate the snailís intestine
 . Genera
Cerithidia and Pironella are important snail hosts in Asia and
the Middle East respectively. The miracidia undergo several developmental
stages in the snail, i.e. sporocysts . Genera
Cerithidia and Pironella are important snail hosts in Asia and
the Middle East respectively. The miracidia undergo several developmental
stages in the snail, i.e. sporocysts
 , rediae , rediae
 , and
cercariae , and
cercariae
 . Many
cercariae are produced from each redia. The cercariae are released from the
snail . Many
cercariae are produced from each redia. The cercariae are released from the
snail  and encyst as metacercariae in the tissues of a suitable fresh/brackish
water fish (second intermediate host)
and encyst as metacercariae in the tissues of a suitable fresh/brackish
water fish (second intermediate host)
 . The
definitive host becomes infected by ingesting undercooked or salted fish
containing metacercariae . The
definitive host becomes infected by ingesting undercooked or salted fish
containing metacercariae
 . After
ingestion, the metacercariae excyst, attach to the mucosa of the small
intestine . After
ingestion, the metacercariae excyst, attach to the mucosa of the small
intestine
 and mature into adults (measuring 1.0 to 1.7 mm by 0.3 to 0.4 mm)
and mature into adults (measuring 1.0 to 1.7 mm by 0.3 to 0.4 mm)
 .
In addition to humans, various fish-eating mammals (e.g., cats and dogs) and
birds can be infected by Heterophyes heterophyes .
In addition to humans, various fish-eating mammals (e.g., cats and dogs) and
birds can be infected by Heterophyes heterophyes
 . . |
|