| |
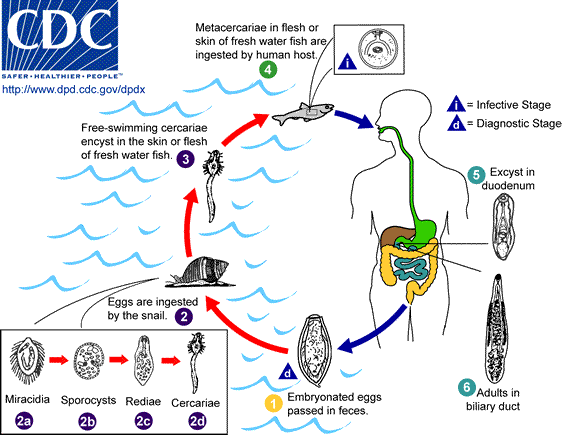
Embryonated eggs are
discharged in the biliary ducts and in the stool
 .
Eggs are ingested by a suitable snail intermediate host .
Eggs are ingested by a suitable snail intermediate host
 ; there
are more than 100 species of snails that can serve as intermediate hosts.
Each egg releases a miracidia ; there
are more than 100 species of snails that can serve as intermediate hosts.
Each egg releases a miracidia
 , which
go through several developmental stages (sporocysts , which
go through several developmental stages (sporocysts
 , rediae , rediae
 , and
cercariae , and
cercariae
 ). The
cercariae are released from the snail and after a short period of
free-swimming time in water, they come in contact and penetrate the flesh of
freshwater fish, where they encyst as metacercariae ). The
cercariae are released from the snail and after a short period of
free-swimming time in water, they come in contact and penetrate the flesh of
freshwater fish, where they encyst as metacercariae
 .
Infection of humans occurs by ingestion of undercooked, salted, pickled, or
smoked freshwater fish .
Infection of humans occurs by ingestion of undercooked, salted, pickled, or
smoked freshwater fish
 . After
ingestion, the metacercariae excyst in the duodenum . After
ingestion, the metacercariae excyst in the duodenum
 and ascend the biliary tract through the ampulla of Vater
and ascend the biliary tract through the ampulla of Vater
 .
Maturation takes approximately 1 month. The adult flukes (measuring 10 to
25 mm by 3 to 5 mm) reside in small and medium sized biliary ducts. In
addition to humans, carnivorous animals can serve as reservoir hosts. .
Maturation takes approximately 1 month. The adult flukes (measuring 10 to
25 mm by 3 to 5 mm) reside in small and medium sized biliary ducts. In
addition to humans, carnivorous animals can serve as reservoir hosts.
|
|