Motility:
Tumbling motility at 26°C
Non-motile at 35° C
![]()
![]()
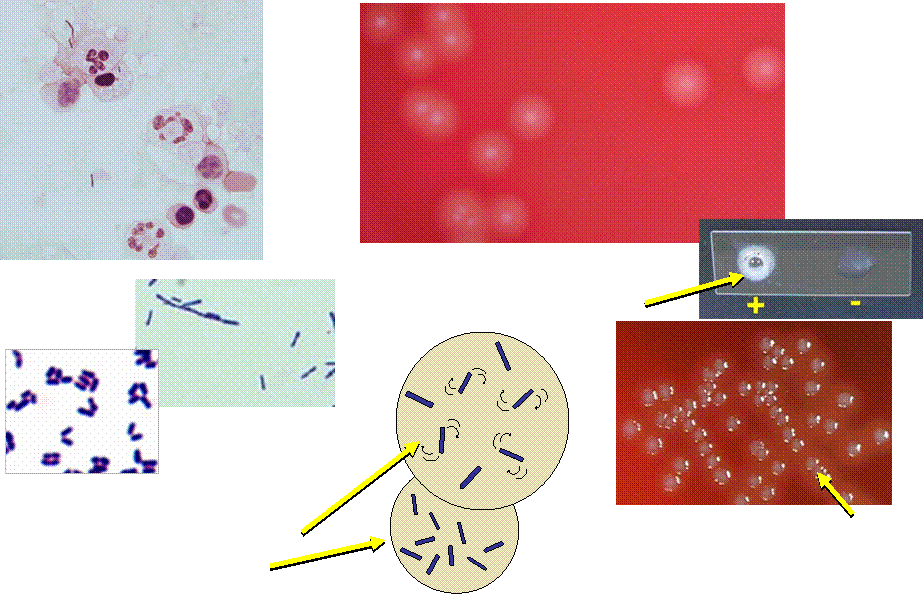
Beta hemolysis does NOT extend
beyond edge of colony
May be short or longer
Colony looks like Group B streptococci.
Differentiate from Group B strep by Gram stain
and positive catalase reaction
CSF showing PMNs, Monocytes, &
Gram positive