Major pathogen in pneumonia, abscesses, skin lesions, blood cultures
@ Ellen Jo Baron 2007




![]()


| Characteristic | B. pseudomallei | B. cepacia | P. stutzeri |
| Wrinkled colony | + | – | Later |
| Gas from Nitrate | + | – | +/- |
| Arginine dihydrolase | + | – | – |
| Musty odor | + | – | – |
Cepacia agar
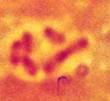
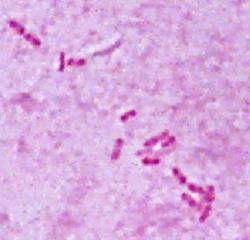
Bipolar-stain Gram - rod
MacConkey: MacConkey agar is a selective medium that inhibits the growth of Gram-positive bateria due to the presence of crystal violet and bile salts. Most Gram-negative bacteria grow well on MacConkey. MacConkey agar also contains neutral red (a pH indicator) and lactose (a disaccharide). Lactose fermenting bacteria or Lactose + bacteria on MacConkey will appear as bright pink colonies. Non-lactose fermenting bacteria will be colorless (or, if they have any color, will be their natural color rather than pink).
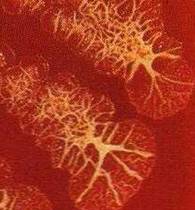
Rough, non-lactose
fermenter on Mac
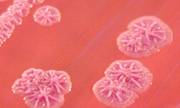
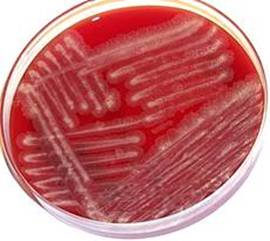
B. cepacia: smooth, pale
greenish colonies on BAP